Local AI Citations, TikTok Explorers, Worthless Reviews, Global Opt-Out

Unpacking Local AI Citations
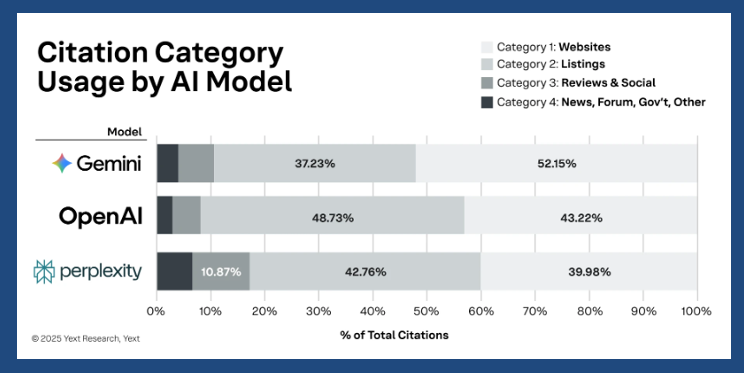
A new analysis, from Yext looks at how location, context and search intent affect which citations appear in AI results. The study critiques brand-level visibility analyses (see Profound) as being superficial and insufficient for local marketers. The study digested nearly 7 million citations from 1.6 million AI answers on OpenAI, Gemini and Perplexity. Yext also examined multiple query types (branded/unbranded, objective/subjective) across four industries (Finance, Food Service, Healthcare, and Retail). It then grouped citations into four categories: websites, listings (directories), review sites and social platforms, and other (news, forums, gov't, etc.). At the highest level, as one might expect, Yext found that citations differ by AI platform, industry and query type. For example, "Gemini shows a strong preference for first-party websites" (52.2%), while "OpenAI relies heavily on listings" (48.7%). Yext also points out that OpenAI draws heavily on Google Business Profiles as well. Each citation category was also rated according to the degree of control the brand or business may have. Websites, for instance, are "fully controllable," while directories are merely "controllable" and review/social sites can be "influenced" but not controlled.